What is Edge Computing?
In short, edge computing focuses on bringing computing closer to where the action happens, as opposed to far away in a central location. Instead of data being transported to an external data centre or public cloud, it’s processed directly on the device on which it was created. That is to say the data is stored at the ‘edge’ of the network.
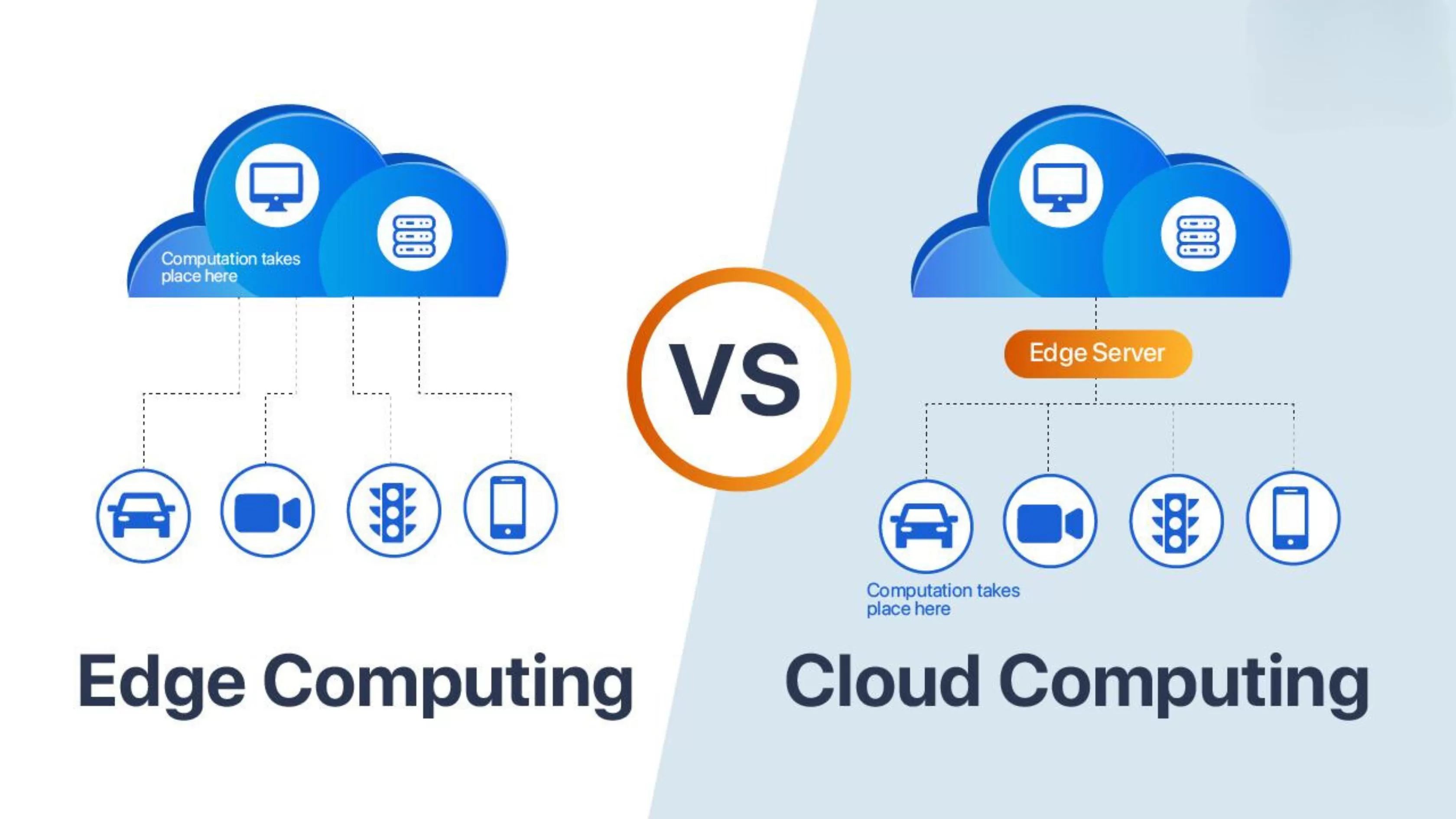
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
The late 90s brought about the first instances of what we now know as cloud computing. Instead of owning and managing physical hardware and infrastructure, cloud computing would allow users to access services such as data storage and processing in a centralised location dubbed the ‘cloud’.
Cloud computing offers a number of advantages, including instant bandwidth increases, less time spent managing data storage issues and increased flexibility in where you use a device. The development of edge computing doesn’t mean cloud computing will soon be obsolete – to get the most out of both concepts, edge computing should only be implemented where it makes sense.
“Edge intelligence refers to the ability to intelligently distribute computing between edge and cloud resource.” – Ryan Martin, principal analyst at ABI Research
Benefits of Edge Computing
Improved Performance
When data is stored close to a device – whether on the device itself or on the network edge – latency is reduced. Latency refers to the delay between a user’s action, and the computer’s response to that action. The higher the latency, the longer you have to wait for data to be transferred – and by bringing the server closer to the device, edge computing reduces latency.
Cost Savings
The reduced latency allowed by edge computing also minimises the use of bandwidth and network resources. The implementation of edge computing technology in the workplace can bring significant cost savings for companies processing large amounts of data, as they will no longer have to pay for external cloud storage.
Data Security
By reducing the amount of data transmitted and processed in the cloud, edge computing can also improve data security. Instead of sending sensitive data back and forth from the cloud, it can be stored and processed in a secure environment, protecting it from cyber attacks and reducing the risk of compromise.
Edge Computing in the Automotive Industry
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and Self-Driving Cars
Edge computing enables ADAS features like collision avoidance and lane assistance by processing sensor data in real-time, enhancing vehicle safety and reducing the potential for accidents. The same technology can be used in self-driving vehicles – the data from cameras and sensors can be processed instantly so real-time decisions can be made regarding navigation.Predictive Maintenance
Edge computing allows vehicles to monitor their own systems and diagnose issues in real-time. This enables predictive maintenance, where maintenance needs are detected early, reducing downtime and preventing costly breakdowns. Edge computing also enables remote diagnostics and over-the-air software updates, reducing the need for in-person service appointments and ensuring vehicles remain up-to-date with the latest features and security patches.Real-Time Traffic and Navigation
Traffic and navigation data, when processed instantly, can provide drivers with real-time updates about traffic, road accidents, road closures and even available parking spaces in car parks. This helps reduce travel time and improve fuel efficiency.Edge Computing in the Automotive Industry

In-Store Customer Analytics
Edge computing enables the real-time analysis of customer data, such as foot traffic, dwell times, and shopping behaviour. This data helps retailers optimise store layouts, product placements, and marketing strategiesInventory Management
Edge devices can monitor inventory levels in real-time, providing automated alerts for restocking and minimising out-of-stock situations. This ensures that customers can find the products they want when they visit a store.Self-Checkout Kiosks
Self-checkout kiosks rely on edge computing to handle transactions efficiently, offering customers a quick and convenient checkout experience.Edge Computing in the Healthcare Industry
Remote Patient Monitoring
Edge computing supports more efficient monitoring of patients’ vital signs, helping healthcare providers track and respond to changes in health conditions promptly. This is especially useful for managing chronic diseases and elderly care, and the data can also be used in predictive analytics to identify potential risks, allowing for early intervention.Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Medical devices such as blood glucose monitors or portable ultrasound machines can use edge computing to process and analyse data locally, offering quick results for immediate decision-making.Smart Health Devices
Smart prosthetics, pacemakers, and other medical devices can process data at the edge, allowing for instant adjustments and improvements to patient comfort. Other wearable smart health devices, like smartwatches and fitness trackers, monitor and process health data locally, providing real-time updates to users which can then be shared with healthcare professionals.Edge Computing in the Gaming Industry
Online Gaming and Streaming
The reduced latency allowed by edge computing provides a smoother, more responsive online gaming experience for players. The issues with lag, long loading times or disconnections which are common when using a cloud-based server to game are minimised, making it a much more enjoyable experience.Content Delivery and Updates
Edge servers can cache and deliver game content, including updates and patches, closer to players. This reduces download times and decreases the load on central servers.AI and Real-Time Game Analytics
Edge computing can support AI-driven game enhancements, such as real-time analysis of player behaviour. This enables dynamic and responsive game environments, where in-game objects and elements can adapt to player actions in real-time. It also allows for real-time detection and thus prevention of cheating in online multiplayer games.Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Edge computing is crucial for VR and AR gaming, as it reduces latency and allows for real-time rendering and processing of complex 3D environments.Edge Computing in the Fintech Industry
Fraud Detection and Prevention
Real-time fraud detection is crucial in fintech. Edge computing can enable the analysis of transaction data on local servers or devices, identifying potentially fraudulent activities more quickly. Multi-factor authentication and biometric data processing can also benefit from edge computing by verifying identity quickly and securely at the point of use.
ATM and Point of Sale (PoS) Terminals
Edge computing can enhance the performance of ATMs and PoS terminals by processing transactions locally – no more waiting for payments to process, even in more rural areas with unreliable network connections. This can also be applied to mobile banking apps.
Customer Service
Edge computing can power chatbots that offer immediate customer support, allowing for more efficient query resolution. It can also help to deliver personalised services like investment recommendations and financial advice by processing customer data locally, ensuring privacy and responsiveness.

At ASPEKT, we’re fascinated by the latest developments in everything digital. For more insights into the ever-evolving digital landscape, visit our Instagram or click here to view the rest of our blogs.
Written by Bethany Piper
Copywriter | ASPEKT
June 2nd, 2023