Written in virtual language, the smart contract can execute and enforce itself independently and automatically depending on a set of predefined criteria. The fundamental benefit of blockchain technology is that it reinforces security, transparency, and trust between signatures, avoiding misunderstandings, falsifications, or revisions, and eliminating the need for middlemen.
Smart contracts have emerged with the aim to use blockchain technology, to simplify the administrative processes and make them paperless where possible. Thus, things like purchasing a house or a car should become easier and quicker with smart contracts.
What are exactly smart contracts?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract in which the conditions of the buyer-seller agreement are directly written into lines of code. The code and the agreements contained within it are dispersed and decentralised over a blockchain network. Transactions are trackable and irreversible, and the code controls the execution.
Smart contracts were first introduced by Nick Szabo, computer scientist and cryptographer when he was a student at the University of Washington. He defined them as ‘’far more functional than their inanimate paper-based ancestors. No use of artificial intelligence is implied. A smart contract is a set of promises, specified in digital form, including protocols within which the parties perform on these promises.’’
Szabo predicted blockchain technology many years before its emergence. He was a visionary, who invented the ‘’Bit Gold’’ a crypto digital currency ten years before the BitCoin apparition.

How does it work?
Currently, Ethereum is the most popular smart contract platform, although it may be operated on a variety of cryptocurrency blockchains, including EOS, Neo, Tezos, Tron, Polkadot, and Algorand. Anyone can initiate a smart contract in a blockchain. Because its code is open and publicly verifiable, any interested party can see exactly what logic a smart contract follows when it receives digital assets.
The steps to complete a smart contract are similar to a blockchain transfer:
- Transaction: A user in the Peer-to-Peer (P2P) initiates a transaction from their blockchain wallet.
- Validation: The transaction arrives at the distributed database, where the identity is confirmed.
- Verification: The transaction, which may be a transfer of funds, is approved.
- Hash & Confirmation: The transaction includes the code that defines what type of transaction is to be executed. The transactions are added as a block within the blockchain. Following this the ?
Once confirmed in a blockchain, a smart contract can hardly be modified or hacked even by its own initiator. Any change in contract status has to follow the same process to be updated.


Why smart contracts are better?
Autonomy and savings
Smart contracts are performed automatically. They do not need brokers or other third parties to confirm the agreement, eliminating the risk of manipulation. Then, the absence of intermediaries in smart contracts results in cost-saving as they are no operational expenses.
Storage & backup
All the documents stored on the blockchain are duplicated multiple times; thus, originals can be restored in the event of any data loss.
Safety & reliability
Smart contracts are encrypted, and with cryptography, they become tamper-proof verifiable records.
Speed & accuracy
Smart contracts are executed immediately through automated tasks, saving hours of various business processes. Then, using smart contracts prevent human errors that can occur with paperwork.
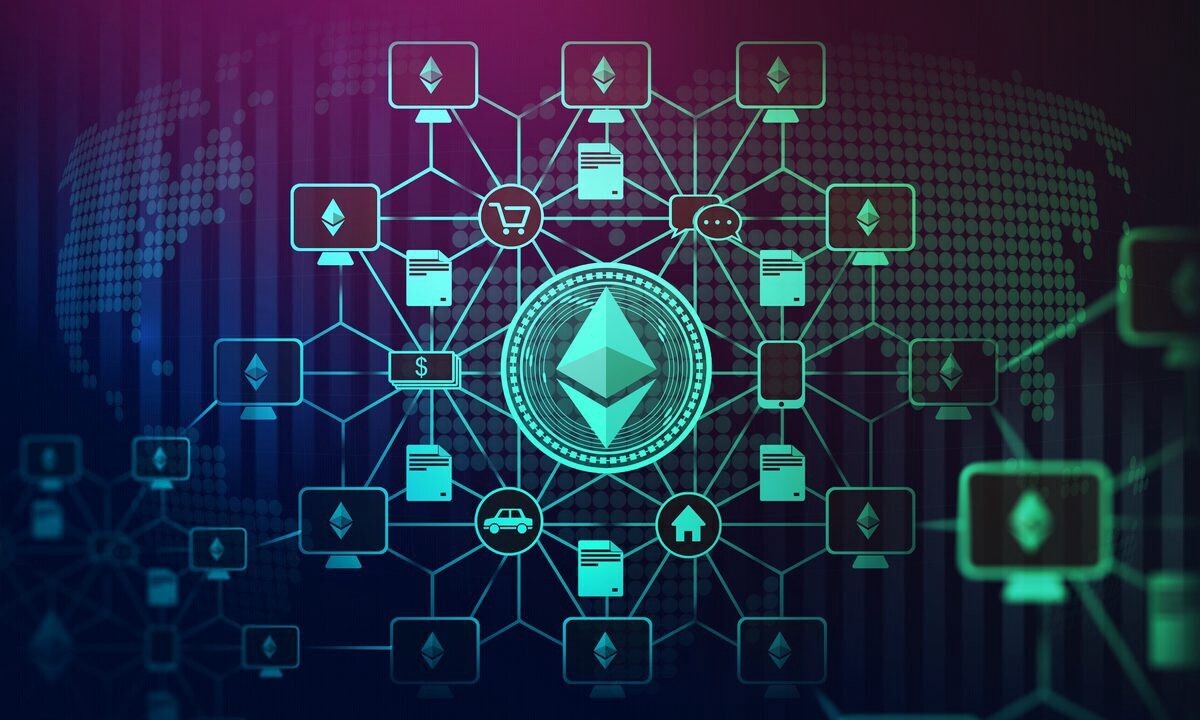

What's next?
Smart contracts were created to remove all the hassle related to administrative paper contracts. They offer a faster, reliable and more secure way to formalise agreements online. To go further, smart contracts aim to provide a secure environment to make the online voting systems less exposed to fraud. Smart contracts and the blockchain are also used to store information in Healthcare, Financial Services and Supply chains to prevent data breaches.
Therefore, smart contracts are something firms must consider as Web3 is emerging as the new decentralised online ecosystem based on blockchain.