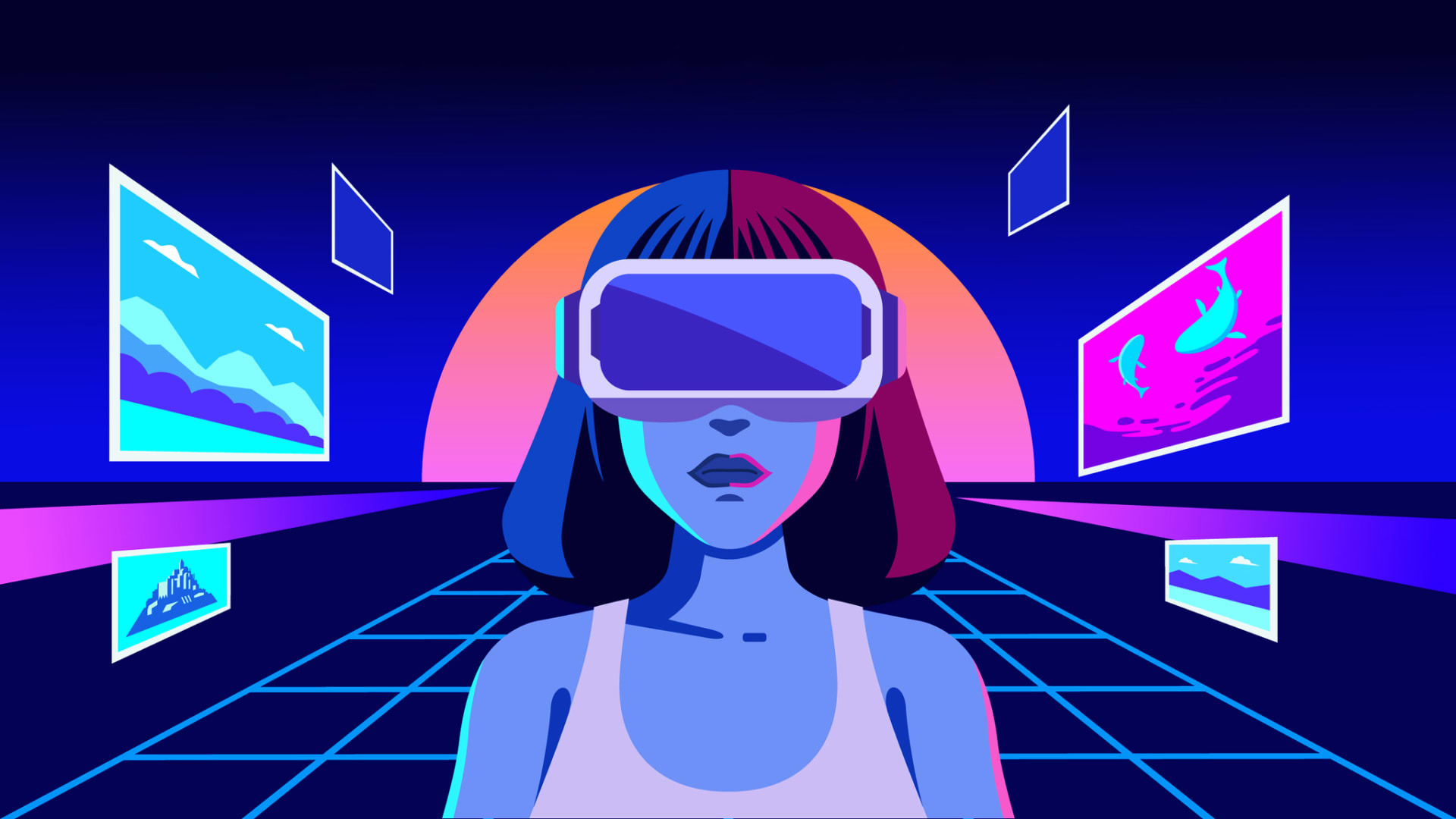
We are sure you must have heard of the metaverse by now; the term was all over social media and blogs following Facebook’s rebranding to Meta in October 2021. Mark Zuckerberg said they wanted the company name to reflect its long-term investment and work on virtual technologies and show that their business and activities extend beyond social media platforms.
Contrary to common assumptions, the metaverse isn’t a new concept. People have been attempting to create immersive and virtual worlds since the 1960s in the movie and gaming industries. We’ll give you a quick and simple explanation of the new phenomenon some people believe is the future of the internet.
What’s the metaverse?
The term ‘’metaverse’’ refers to a simulated cyberspace using augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and blockchain technology, all combined with social media features. This mirrorworld recreates a digital copy of people, places and things.
The Metaverse is a three-dimensional virtual world where people will be able to socialise, game, work and interact in the form of avatars without leaving the comfort of their homes. The current version of the internet is 2D. People browse and scroll through it on computers, phones, and other interactive screens. The Metaverse promises to let you walk through it using devices like AR glasses and VR headsets.

What does it change?
The implication of tech giants like Facebook and Google’s interest in the Metaverse shows how much of an impact this may have on the current internet system. Google has been quietly investing in the Metaverse since 2015. Indeed, the company changed its parent name to Alphabet to reflect its activity in various industries, including Metaverse.
Alphabet CEO numerously spoke about the company’s investment in augmented reality (AR). They explore and consider the idea to implement YouTube and Google Maps in the Metaverse. In 2011, Google created Google Glass, AR connected spectacles that promised to blend the real world with the virtual. This was a significant failure for the company as they learned that they had two obstacles, the tech wasn’t ready, and neither were people.
The Metaverse won’t only include ‘’real people’’; Artificial Intelligence like bots or virtual agents will be included in this new world. Experts believe that things happening in the Metaverse will affect events in the real world. For instance, using AR or VR to attend virtual concerts or sports games or test things before buying them. Ikea was one of the first companies to use AR tech to help customers visualise furniture in their room before purchasing them. Thus, companies offer immersive retail experiences and allow you to try on things like prescription glasses, make-up products or other tech gadgets from anywhere.
Sectors such as Healthcare or Education could benefit from Metaverse. Indeed, this digital twin will offer new opportunities for learning and training, like training for surgical operations or using VR to help people face their fears in therapy. Travel companies want to use it to attract tourists to specific destinations or hotels and increase their profit. Many inventors and entrepreneurs already use it to create a digital replica of their invention and show how it will look in the real world (skeuomorphic design).


Examples of metaverse
Decentraland was one of the pioneers to launch its metaverse in 2020. The platform is a VR space where users can interact with each other, create content and earn money through investments in NFTs and virtual real estate. Decentraland is decentralised and operates with its own cryptocurrency creating a new world and a new economy in the virtual world.
Sandbox, a multiplayer game, launched in 2012 and rebranded in 2018 as a VR game. Players can create games, participate in events, socialise, purchase land and walk through the virtual world. Other metaverses include Cryptovoxels, Somnium Space, Roblox and Bloktopia. They all offer users freedom to generate content and sometimes program their own experience. Finally, many of them include an internal economy through which users could earn tokens or digital coins and trade them in both virtual and physical worlds. NFTs and cryptocurrencies were added to Decentraland and Sandbox; they serve as proof of ownership for digital objects or monetisation tools

What's next?
Metaverse is an overlay of the physical world, blurring between virtual and reality. The aim is to create an immersive iteration of the internet. Metaverse advocates believe it will be an excellent substitute for current social platforms, making you feel even closer to people online. For instance, you could use metaverse to attend real-life meetings as a hologram.
Metaverse has an enormous potential in terms of monetisation. GAFAs have understood this. Following the rebranding, Meta group (formerly Facebook) launched Horizon Worlds, a VR platform where users can navigate as avatars and developers create new digital worlds. Public personalities like Snoop Dog have also invested in the metaverse; the rapper is building his own virtual world in Sandbox metaverse called Snoopverse. Unbelievably, a user spent $450,000 buying a digital plot of land in the rapper’s future virtual world. In April 2022, he also released a music and video clip entirely shot in the Snoopverse, inviting his fans to join him in his virtual world.
Nobody knows if the metaverse will be a single virtual world or several ones, but believers hope they will all be connected. While we are not sure what will become the new web, we are interested in what will be discovered along the way.
Written by Germaine
Copywriter | ASPEKT
November 03, 2022